It was once the muddy water that caught Stefan Talke’s eye. In the mid-2000s Talke used to be a postdoctoral pupil at Utrecht University, analyzing the river Ems that empties into the North Sea between Germany and the Netherlands. Decades earlier, engineers had begun dredging components of the Ems so that newly constructed ships may want to navigate it from a shipyard upriver.
But these modifications additionally modified the rhythm with which tides ebbed and flowed into the river from the sea. Those moving tides stirred up sediment from the river backside and muddied its waters. Over the ultimate one hundred twenty years the tidal vary – the distance between excessive and low tide – has quintupled in the Ems estuary.
“I had usually assumed tides have been constant,” says Talke, now an oceanographer at California Polytechnic State University in San Luis Obispo. “That’s why we have tide tables.” He used to be amazed to discover, he says, that no longer solely should tides endure long-term changes, however that they ought to trade via so much.
Most humans suppose of tides as ordinary and predictable – the upward jab and fall of coastal waters, precipitated by using the gravitational tug of the Moon and the Sun, forecast down to the minute with a mariner’s tide table. But oceanographers have these days commenced to recognise that tides in many locations round the world are present process splendid changes, in approaches that can’t be defined via interactions amongst celestial bodies.
Rather, it is human beings that are altering the tides. Dredging river channels like the Ems or filling in coastal wetlands can set off shifts. The nature of these shifts is complicated. In some areas the tidal vary grows extra dramatic, whereas in others it shrinks. Either way, the transferring tides have large implications for lots of thousands and thousands of coastal residents.
Perhaps the largest project is how altering tides may add to the dangers of sea stage rise.
As human beings burn greater fossil fuels and put extra heat-trapping greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, international warming is melting ice caps and inflicting the extent of the oceans to expand. In many coastal cities, seawater is now lapping greater than it ever has. Changing tides should add to that hassle and go away some coasts at even higher danger of flooding. “What human beings don’t recognise is that if tidal vary is increasing, it will exacerbate that even more,” says Ivan Haigh, an oceanographer at the University of Southampton, UK.
The way the water strikes throughout the basin is changing, which is having pretty a profound impact on the tides – Ivan Haigh
Engineers have acknowledged for at least a century that tides can alternate locally. In 1899, builders estimated that tides would make bigger in the river Ems upstream from a weir they deliberate to construct. (After the weir used to be built, the tides did expand about as lots as they have been expecting.)
But solely lately have scientists accrued modern, specific tide-gauge facts from round the world, displaying simply how enormous tidal modifications have become. “It wasn’t actually till about 10 years in the past that we commenced to admire that it’s taking place on a plenty wider level,” says Haigh.
Tides come in countless flavours, which can all eventually be traced again to interactions between the Moon, the Sun and Earth. Each tidal cycle reasons coastal waters to upward jab and fall in a predictable pattern, dictated by way of the orbits of these bodies.
The gravitational tugs of the Moon and the Sun don’t trade over the brief term. But what does trade is the way the Earth’s waters reply to that tugging. Think of tides as repeating waves that soar off landmasses and slosh upriver – every now and then visiting lots of kilo-metres inland, as they do in South America’s Amazon River, the place surfers journey the tidal waves. If you exchange the geometry of the land they slosh round in, you alternate the tides, says Talke.
“It’s like having a one-of-a-kind dimension or structure of a bathtub or a swimming pool – you’d assume water to drift otherwise in it,” he says.
In that sense, it’s no longer terribly shocking that tides have modified dramatically in locations the place humans have modified the structure of the underwater landscape. Along the Cape Fear river in North Carolina, dredging to deepen a ship channel has brought about the tidal vary in the town of Wilmington to double, to 1.55m (5.1ft), considering that the 1880s. The identical is proper for Jacksonville, Florida, which sits alongside the dredged St Johns River.
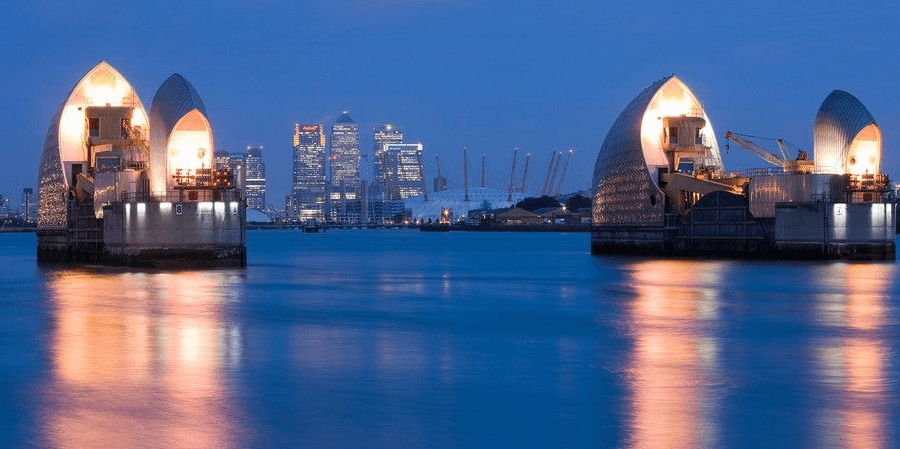
In Sacramento, California, tides disappeared in the late 1800s after mining from the Gold Rush despatched silt speeding downstream. Later, dredging of the Sacramento River added the tides back. And in the Thames estuary that runs thru London, engineers have narrowed and deepened the river over centuries – its tidal vary has multiplied from round 2m (6.6ft) in the time of the Romans to round 8m (26.2ft) in the Victorian age.
Adding dikes or piers motives water to drift extra turbulently and dissipate its electricity faster, probable dampening tides
Tidal adjustments additionally take place each time flowing water generates greater or much less turbulent power as it strikes thru the landscape, write Talke and a colleague in the current Annual Review of Marine Science. Stripping away underwater plant life reduces drag and lets waters glide greater freely, doubtlessly permitting tides to increase. Adding dikes or piers reasons water to drift greater turbulently and dissipate its power faster, probably dampening tides.
Water depth is any other necessary issue in tidal changes, says Haigh. Because tides propagate as shallow-water waves, they alternate the most anywhere the water is additionally shallow. That’s why the Bay of Fundy, between New Brunswick and Nova Scotia in Canada, has some of the most dramatic tidal levels in the world, with waters rising and falling greater than 11m (36ft) every day. Shallow spots like this are probably to see giant modifications in tidal vary as sea ranges rise, Haigh says.
“The way the water strikes throughout the basin is changing, which is having pretty a profound impact on the tides,” he says.
Changing tides have an effect on coastal residents in many ways. Someone who wishes to sail a tall ship beneath a brief bridge has to wait for simply the proper tidal stipulations whilst all and sundry who needs to construct a riverfront domestic in an estuary has to understand precisely the place the high-tide mark is. Engineers designing a tidal-energy device want to comprehend how a whole lot power they can extract from the water flows. And that’s the place the find out about of altering tides can assist human beings put together for a altering world.
Perhaps most importantly, engineers can analyse altering tides to higher layout for future sea degree rise. One current find out about regarded at the low-lying Pearl River Delta in southern China, which is domestic to extra than 60 million people. Michela De Dominicis, an oceanographer at the National Oceanography Centre in Liverpool, UK, and her colleagues calculated how plenty tidal stages would shift for a range of future situations of sea stage rise.
If sea degree have been to upward shove between 0.5m and 2.1m (1.6-6.9ft) in the delta, then cities in its upstream reaches would see tidal will increase between 0.1m and 0.5m (0.3ft and 1.6ft), the scientists found. Add these numbers collectively and it appears as if water tiers should go up between 0.6m and 2.6m (2-8.5ft).
Several cities in the delta, which includes Guangzhou and Shenzhen, are amongst the world’s most inclined to rising water levels, says De Dominicis. Knowing how excessive the water tiers should upward push can assist planners construct higher limitations and different coastal defences.
Researchers are additionally the usage of laptop fashions to analyse how altering tides and rising sea stages may have an effect on different kinds of coastal flooding. A hurricane’s storm surge, for instance, frequently responds to the altering panorama a great deal as tides do.
In 2016, Talke and his colleagues analysed how storm surge may trade in the Cape Fear River estuary alongside with the altering tides. They calculated that dredging of the ship channel has correctly worsened the doable harm posed via a Category 5 typhoon and raised the best possible feasible water ranges in Wilmington through 1.8m (5.9ft).
In 2018, when Category 1 Hurricane Florence slammed into Wilmington, water tiers did certainly attain a document 1.1m (3.6ft) above excessive tide. That’s why appreciation altering tides is critical to making ready for the future, Talke says. People are going to proceed to dredge channels and fill in wetlands and in any other case alter our coastal surroundings. Bit by using bit, every change shifts the world in which we live.
ABOUT ME


I could look back at my life and get a good story out of it. It's a picture of somebody trying to figure things out.
POPULAR POSTS
Hollywood Movies
Categories
- Health 10
- Science & Technology 7
- Sports 9
- Work Life 7
- World 25
Comments
Recent
Post Top Ad

Socialize
category2
Fashion
Music
News
Food
Sports
Food
Technology
Featured
Videos
Popular Posts
Contact Us
Ticker
6/recent/ticker-posts
Tags Clouds
It was once the muddy water that caught Stefan Talke’s eye. In the mid-2000s Talke used to be a postdoctoral pupil at Utrecht University, analyzing the river Ems that empties into the North Sea between Germany and the Netherlands. Decades earlier, engineers had begun dredging components of the Ems so that newly constructed ships may want to navigate it from a shipyard upriver.
But these modifications additionally modified the rhythm with which tides ebbed and flowed into the river from the sea. Those moving tides stirred up sediment from the river backside and muddied its waters. Over the ultimate one hundred twenty years the tidal vary – the distance between excessive and low tide – has quintupled in the Ems estuary.
“I had usually assumed tides have been constant,” says Talke, now an oceanographer at California Polytechnic State University in San Luis Obispo. “That’s why we have tide tables.” He used to be amazed to discover, he says, that no longer solely should tides endure long-term changes, however that they ought to trade via so much.
Most humans suppose of tides as ordinary and predictable – the upward jab and fall of coastal waters, precipitated by using the gravitational tug of the Moon and the Sun, forecast down to the minute with a mariner’s tide table. But oceanographers have these days commenced to recognise that tides in many locations round the world are present process splendid changes, in approaches that can’t be defined via interactions amongst celestial bodies.
Rather, it is human beings that are altering the tides. Dredging river channels like the Ems or filling in coastal wetlands can set off shifts. The nature of these shifts is complicated. In some areas the tidal vary grows extra dramatic, whereas in others it shrinks. Either way, the transferring tides have large implications for lots of thousands and thousands of coastal residents.
Perhaps the largest project is how altering tides may add to the dangers of sea stage rise.
As human beings burn greater fossil fuels and put extra heat-trapping greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, international warming is melting ice caps and inflicting the extent of the oceans to expand. In many coastal cities, seawater is now lapping greater than it ever has. Changing tides should add to that hassle and go away some coasts at even higher danger of flooding. “What human beings don’t recognise is that if tidal vary is increasing, it will exacerbate that even more,” says Ivan Haigh, an oceanographer at the University of Southampton, UK.
The way the water strikes throughout the basin is changing, which is having pretty a profound impact on the tides – Ivan Haigh
Engineers have acknowledged for at least a century that tides can alternate locally. In 1899, builders estimated that tides would make bigger in the river Ems upstream from a weir they deliberate to construct. (After the weir used to be built, the tides did expand about as lots as they have been expecting.)
But solely lately have scientists accrued modern, specific tide-gauge facts from round the world, displaying simply how enormous tidal modifications have become. “It wasn’t actually till about 10 years in the past that we commenced to admire that it’s taking place on a plenty wider level,” says Haigh.
Tides come in countless flavours, which can all eventually be traced again to interactions between the Moon, the Sun and Earth. Each tidal cycle reasons coastal waters to upward jab and fall in a predictable pattern, dictated by way of the orbits of these bodies.
The gravitational tugs of the Moon and the Sun don’t trade over the brief term. But what does trade is the way the Earth’s waters reply to that tugging. Think of tides as repeating waves that soar off landmasses and slosh upriver – every now and then visiting lots of kilo-metres inland, as they do in South America’s Amazon River, the place surfers journey the tidal waves. If you exchange the geometry of the land they slosh round in, you alternate the tides, says Talke.
“It’s like having a one-of-a-kind dimension or structure of a bathtub or a swimming pool – you’d assume water to drift otherwise in it,” he says.
In that sense, it’s no longer terribly shocking that tides have modified dramatically in locations the place humans have modified the structure of the underwater landscape. Along the Cape Fear river in North Carolina, dredging to deepen a ship channel has brought about the tidal vary in the town of Wilmington to double, to 1.55m (5.1ft), considering that the 1880s. The identical is proper for Jacksonville, Florida, which sits alongside the dredged St Johns River.
In Sacramento, California, tides disappeared in the late 1800s after mining from the Gold Rush despatched silt speeding downstream. Later, dredging of the Sacramento River added the tides back. And in the Thames estuary that runs thru London, engineers have narrowed and deepened the river over centuries – its tidal vary has multiplied from round 2m (6.6ft) in the time of the Romans to round 8m (26.2ft) in the Victorian age.
Adding dikes or piers motives water to drift extra turbulently and dissipate its electricity faster, probable dampening tides
Tidal adjustments additionally take place each time flowing water generates greater or much less turbulent power as it strikes thru the landscape, write Talke and a colleague in the current Annual Review of Marine Science. Stripping away underwater plant life reduces drag and lets waters glide greater freely, doubtlessly permitting tides to increase. Adding dikes or piers reasons water to drift greater turbulently and dissipate its power faster, probably dampening tides.
Water depth is any other necessary issue in tidal changes, says Haigh. Because tides propagate as shallow-water waves, they alternate the most anywhere the water is additionally shallow. That’s why the Bay of Fundy, between New Brunswick and Nova Scotia in Canada, has some of the most dramatic tidal levels in the world, with waters rising and falling greater than 11m (36ft) every day. Shallow spots like this are probably to see giant modifications in tidal vary as sea ranges rise, Haigh says.
“The way the water strikes throughout the basin is changing, which is having pretty a profound impact on the tides,” he says.
Changing tides have an effect on coastal residents in many ways. Someone who wishes to sail a tall ship beneath a brief bridge has to wait for simply the proper tidal stipulations whilst all and sundry who needs to construct a riverfront domestic in an estuary has to understand precisely the place the high-tide mark is. Engineers designing a tidal-energy device want to comprehend how a whole lot power they can extract from the water flows. And that’s the place the find out about of altering tides can assist human beings put together for a altering world.
Perhaps most importantly, engineers can analyse altering tides to higher layout for future sea degree rise. One current find out about regarded at the low-lying Pearl River Delta in southern China, which is domestic to extra than 60 million people. Michela De Dominicis, an oceanographer at the National Oceanography Centre in Liverpool, UK, and her colleagues calculated how plenty tidal stages would shift for a range of future situations of sea stage rise.
If sea degree have been to upward shove between 0.5m and 2.1m (1.6-6.9ft) in the delta, then cities in its upstream reaches would see tidal will increase between 0.1m and 0.5m (0.3ft and 1.6ft), the scientists found. Add these numbers collectively and it appears as if water tiers should go up between 0.6m and 2.6m (2-8.5ft).
Several cities in the delta, which includes Guangzhou and Shenzhen, are amongst the world’s most inclined to rising water levels, says De Dominicis. Knowing how excessive the water tiers should upward push can assist planners construct higher limitations and different coastal defences.
Researchers are additionally the usage of laptop fashions to analyse how altering tides and rising sea stages may have an effect on different kinds of coastal flooding. A hurricane’s storm surge, for instance, frequently responds to the altering panorama a great deal as tides do.
In 2016, Talke and his colleagues analysed how storm surge may trade in the Cape Fear River estuary alongside with the altering tides. They calculated that dredging of the ship channel has correctly worsened the doable harm posed via a Category 5 typhoon and raised the best possible feasible water ranges in Wilmington through 1.8m (5.9ft).
In 2018, when Category 1 Hurricane Florence slammed into Wilmington, water tiers did certainly attain a document 1.1m (3.6ft) above excessive tide. That’s why appreciation altering tides is critical to making ready for the future, Talke says. People are going to proceed to dredge channels and fill in wetlands and in any other case alter our coastal surroundings. Bit by using bit, every change shifts the world in which we live.
1 comments:

Next my spirit heated one, for a cheese fondue, because it is a ceramic pot. fondue set
ReplyDelete
It was once the muddy water that caught Stefan Talke’s eye. In the mid-2000s Talke used to be a postdoctoral pupil at Utrecht University, analyzing the river Ems that empties into the North Sea between Germany and the Netherlands. Decades earlier, engineers had begun dredging components of the Ems so that newly constructed ships may want to navigate it from a shipyard upriver.
But these modifications additionally modified the rhythm with which tides ebbed and flowed into the river from the sea. Those moving tides stirred up sediment from the river backside and muddied its waters. Over the ultimate one hundred twenty years the tidal vary – the distance between excessive and low tide – has quintupled in the Ems estuary.
“I had usually assumed tides have been constant,” says Talke, now an oceanographer at California Polytechnic State University in San Luis Obispo. “That’s why we have tide tables.” He used to be amazed to discover, he says, that no longer solely should tides endure long-term changes, however that they ought to trade via so much.
Most humans suppose of tides as ordinary and predictable – the upward jab and fall of coastal waters, precipitated by using the gravitational tug of the Moon and the Sun, forecast down to the minute with a mariner’s tide table. But oceanographers have these days commenced to recognise that tides in many locations round the world are present process splendid changes, in approaches that can’t be defined via interactions amongst celestial bodies.
Rather, it is human beings that are altering the tides. Dredging river channels like the Ems or filling in coastal wetlands can set off shifts. The nature of these shifts is complicated. In some areas the tidal vary grows extra dramatic, whereas in others it shrinks. Either way, the transferring tides have large implications for lots of thousands and thousands of coastal residents.
Perhaps the largest project is how altering tides may add to the dangers of sea stage rise.
As human beings burn greater fossil fuels and put extra heat-trapping greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, international warming is melting ice caps and inflicting the extent of the oceans to expand. In many coastal cities, seawater is now lapping greater than it ever has. Changing tides should add to that hassle and go away some coasts at even higher danger of flooding. “What human beings don’t recognise is that if tidal vary is increasing, it will exacerbate that even more,” says Ivan Haigh, an oceanographer at the University of Southampton, UK.
The way the water strikes throughout the basin is changing, which is having pretty a profound impact on the tides – Ivan Haigh
Engineers have acknowledged for at least a century that tides can alternate locally. In 1899, builders estimated that tides would make bigger in the river Ems upstream from a weir they deliberate to construct. (After the weir used to be built, the tides did expand about as lots as they have been expecting.)
But solely lately have scientists accrued modern, specific tide-gauge facts from round the world, displaying simply how enormous tidal modifications have become. “It wasn’t actually till about 10 years in the past that we commenced to admire that it’s taking place on a plenty wider level,” says Haigh.
Tides come in countless flavours, which can all eventually be traced again to interactions between the Moon, the Sun and Earth. Each tidal cycle reasons coastal waters to upward jab and fall in a predictable pattern, dictated by way of the orbits of these bodies.
The gravitational tugs of the Moon and the Sun don’t trade over the brief term. But what does trade is the way the Earth’s waters reply to that tugging. Think of tides as repeating waves that soar off landmasses and slosh upriver – every now and then visiting lots of kilo-metres inland, as they do in South America’s Amazon River, the place surfers journey the tidal waves. If you exchange the geometry of the land they slosh round in, you alternate the tides, says Talke.
“It’s like having a one-of-a-kind dimension or structure of a bathtub or a swimming pool – you’d assume water to drift otherwise in it,” he says.
In that sense, it’s no longer terribly shocking that tides have modified dramatically in locations the place humans have modified the structure of the underwater landscape. Along the Cape Fear river in North Carolina, dredging to deepen a ship channel has brought about the tidal vary in the town of Wilmington to double, to 1.55m (5.1ft), considering that the 1880s. The identical is proper for Jacksonville, Florida, which sits alongside the dredged St Johns River.
In Sacramento, California, tides disappeared in the late 1800s after mining from the Gold Rush despatched silt speeding downstream. Later, dredging of the Sacramento River added the tides back. And in the Thames estuary that runs thru London, engineers have narrowed and deepened the river over centuries – its tidal vary has multiplied from round 2m (6.6ft) in the time of the Romans to round 8m (26.2ft) in the Victorian age.
Adding dikes or piers motives water to drift extra turbulently and dissipate its electricity faster, probable dampening tides
Tidal adjustments additionally take place each time flowing water generates greater or much less turbulent power as it strikes thru the landscape, write Talke and a colleague in the current Annual Review of Marine Science. Stripping away underwater plant life reduces drag and lets waters glide greater freely, doubtlessly permitting tides to increase. Adding dikes or piers reasons water to drift greater turbulently and dissipate its power faster, probably dampening tides.
Water depth is any other necessary issue in tidal changes, says Haigh. Because tides propagate as shallow-water waves, they alternate the most anywhere the water is additionally shallow. That’s why the Bay of Fundy, between New Brunswick and Nova Scotia in Canada, has some of the most dramatic tidal levels in the world, with waters rising and falling greater than 11m (36ft) every day. Shallow spots like this are probably to see giant modifications in tidal vary as sea ranges rise, Haigh says.
“The way the water strikes throughout the basin is changing, which is having pretty a profound impact on the tides,” he says.
Changing tides have an effect on coastal residents in many ways. Someone who wishes to sail a tall ship beneath a brief bridge has to wait for simply the proper tidal stipulations whilst all and sundry who needs to construct a riverfront domestic in an estuary has to understand precisely the place the high-tide mark is. Engineers designing a tidal-energy device want to comprehend how a whole lot power they can extract from the water flows. And that’s the place the find out about of altering tides can assist human beings put together for a altering world.
Perhaps most importantly, engineers can analyse altering tides to higher layout for future sea degree rise. One current find out about regarded at the low-lying Pearl River Delta in southern China, which is domestic to extra than 60 million people. Michela De Dominicis, an oceanographer at the National Oceanography Centre in Liverpool, UK, and her colleagues calculated how plenty tidal stages would shift for a range of future situations of sea stage rise.
If sea degree have been to upward shove between 0.5m and 2.1m (1.6-6.9ft) in the delta, then cities in its upstream reaches would see tidal will increase between 0.1m and 0.5m (0.3ft and 1.6ft), the scientists found. Add these numbers collectively and it appears as if water tiers should go up between 0.6m and 2.6m (2-8.5ft).
Several cities in the delta, which includes Guangzhou and Shenzhen, are amongst the world’s most inclined to rising water levels, says De Dominicis. Knowing how excessive the water tiers should upward push can assist planners construct higher limitations and different coastal defences.
Researchers are additionally the usage of laptop fashions to analyse how altering tides and rising sea stages may have an effect on different kinds of coastal flooding. A hurricane’s storm surge, for instance, frequently responds to the altering panorama a great deal as tides do.
In 2016, Talke and his colleagues analysed how storm surge may trade in the Cape Fear River estuary alongside with the altering tides. They calculated that dredging of the ship channel has correctly worsened the doable harm posed via a Category 5 typhoon and raised the best possible feasible water ranges in Wilmington through 1.8m (5.9ft).
In 2018, when Category 1 Hurricane Florence slammed into Wilmington, water tiers did certainly attain a document 1.1m (3.6ft) above excessive tide. That’s why appreciation altering tides is critical to making ready for the future, Talke says. People are going to proceed to dredge channels and fill in wetlands and in any other case alter our coastal surroundings. Bit by using bit, every change shifts the world in which we live.
1 comments:

Next my spirit heated one, for a cheese fondue, because it is a ceramic pot. fondue set
ReplyDelete
Fashion
It was once the muddy water that caught Stefan Talke’s eye. In the mid-2000s Talke used to be a postdoctoral pupil at Utrecht University, analyzing the river Ems that empties into the North Sea between Germany and the Netherlands. Decades earlier, engineers had begun dredging components of the Ems so that newly constructed ships may want to navigate it from a shipyard upriver.
But these modifications additionally modified the rhythm with which tides ebbed and flowed into the river from the sea. Those moving tides stirred up sediment from the river backside and muddied its waters. Over the ultimate one hundred twenty years the tidal vary – the distance between excessive and low tide – has quintupled in the Ems estuary.
“I had usually assumed tides have been constant,” says Talke, now an oceanographer at California Polytechnic State University in San Luis Obispo. “That’s why we have tide tables.” He used to be amazed to discover, he says, that no longer solely should tides endure long-term changes, however that they ought to trade via so much.
Most humans suppose of tides as ordinary and predictable – the upward jab and fall of coastal waters, precipitated by using the gravitational tug of the Moon and the Sun, forecast down to the minute with a mariner’s tide table. But oceanographers have these days commenced to recognise that tides in many locations round the world are present process splendid changes, in approaches that can’t be defined via interactions amongst celestial bodies.
Rather, it is human beings that are altering the tides. Dredging river channels like the Ems or filling in coastal wetlands can set off shifts. The nature of these shifts is complicated. In some areas the tidal vary grows extra dramatic, whereas in others it shrinks. Either way, the transferring tides have large implications for lots of thousands and thousands of coastal residents.
Perhaps the largest project is how altering tides may add to the dangers of sea stage rise.
As human beings burn greater fossil fuels and put extra heat-trapping greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, international warming is melting ice caps and inflicting the extent of the oceans to expand. In many coastal cities, seawater is now lapping greater than it ever has. Changing tides should add to that hassle and go away some coasts at even higher danger of flooding. “What human beings don’t recognise is that if tidal vary is increasing, it will exacerbate that even more,” says Ivan Haigh, an oceanographer at the University of Southampton, UK.
The way the water strikes throughout the basin is changing, which is having pretty a profound impact on the tides – Ivan Haigh
Engineers have acknowledged for at least a century that tides can alternate locally. In 1899, builders estimated that tides would make bigger in the river Ems upstream from a weir they deliberate to construct. (After the weir used to be built, the tides did expand about as lots as they have been expecting.)
But solely lately have scientists accrued modern, specific tide-gauge facts from round the world, displaying simply how enormous tidal modifications have become. “It wasn’t actually till about 10 years in the past that we commenced to admire that it’s taking place on a plenty wider level,” says Haigh.
Tides come in countless flavours, which can all eventually be traced again to interactions between the Moon, the Sun and Earth. Each tidal cycle reasons coastal waters to upward jab and fall in a predictable pattern, dictated by way of the orbits of these bodies.
The gravitational tugs of the Moon and the Sun don’t trade over the brief term. But what does trade is the way the Earth’s waters reply to that tugging. Think of tides as repeating waves that soar off landmasses and slosh upriver – every now and then visiting lots of kilo-metres inland, as they do in South America’s Amazon River, the place surfers journey the tidal waves. If you exchange the geometry of the land they slosh round in, you alternate the tides, says Talke.
“It’s like having a one-of-a-kind dimension or structure of a bathtub or a swimming pool – you’d assume water to drift otherwise in it,” he says.
In that sense, it’s no longer terribly shocking that tides have modified dramatically in locations the place humans have modified the structure of the underwater landscape. Along the Cape Fear river in North Carolina, dredging to deepen a ship channel has brought about the tidal vary in the town of Wilmington to double, to 1.55m (5.1ft), considering that the 1880s. The identical is proper for Jacksonville, Florida, which sits alongside the dredged St Johns River.
In Sacramento, California, tides disappeared in the late 1800s after mining from the Gold Rush despatched silt speeding downstream. Later, dredging of the Sacramento River added the tides back. And in the Thames estuary that runs thru London, engineers have narrowed and deepened the river over centuries – its tidal vary has multiplied from round 2m (6.6ft) in the time of the Romans to round 8m (26.2ft) in the Victorian age.
Adding dikes or piers motives water to drift extra turbulently and dissipate its electricity faster, probable dampening tides
Tidal adjustments additionally take place each time flowing water generates greater or much less turbulent power as it strikes thru the landscape, write Talke and a colleague in the current Annual Review of Marine Science. Stripping away underwater plant life reduces drag and lets waters glide greater freely, doubtlessly permitting tides to increase. Adding dikes or piers reasons water to drift greater turbulently and dissipate its power faster, probably dampening tides.
Water depth is any other necessary issue in tidal changes, says Haigh. Because tides propagate as shallow-water waves, they alternate the most anywhere the water is additionally shallow. That’s why the Bay of Fundy, between New Brunswick and Nova Scotia in Canada, has some of the most dramatic tidal levels in the world, with waters rising and falling greater than 11m (36ft) every day. Shallow spots like this are probably to see giant modifications in tidal vary as sea ranges rise, Haigh says.
“The way the water strikes throughout the basin is changing, which is having pretty a profound impact on the tides,” he says.
Changing tides have an effect on coastal residents in many ways. Someone who wishes to sail a tall ship beneath a brief bridge has to wait for simply the proper tidal stipulations whilst all and sundry who needs to construct a riverfront domestic in an estuary has to understand precisely the place the high-tide mark is. Engineers designing a tidal-energy device want to comprehend how a whole lot power they can extract from the water flows. And that’s the place the find out about of altering tides can assist human beings put together for a altering world.
Perhaps most importantly, engineers can analyse altering tides to higher layout for future sea degree rise. One current find out about regarded at the low-lying Pearl River Delta in southern China, which is domestic to extra than 60 million people. Michela De Dominicis, an oceanographer at the National Oceanography Centre in Liverpool, UK, and her colleagues calculated how plenty tidal stages would shift for a range of future situations of sea stage rise.
If sea degree have been to upward shove between 0.5m and 2.1m (1.6-6.9ft) in the delta, then cities in its upstream reaches would see tidal will increase between 0.1m and 0.5m (0.3ft and 1.6ft), the scientists found. Add these numbers collectively and it appears as if water tiers should go up between 0.6m and 2.6m (2-8.5ft).
Several cities in the delta, which includes Guangzhou and Shenzhen, are amongst the world’s most inclined to rising water levels, says De Dominicis. Knowing how excessive the water tiers should upward push can assist planners construct higher limitations and different coastal defences.
Researchers are additionally the usage of laptop fashions to analyse how altering tides and rising sea stages may have an effect on different kinds of coastal flooding. A hurricane’s storm surge, for instance, frequently responds to the altering panorama a great deal as tides do.
In 2016, Talke and his colleagues analysed how storm surge may trade in the Cape Fear River estuary alongside with the altering tides. They calculated that dredging of the ship channel has correctly worsened the doable harm posed via a Category 5 typhoon and raised the best possible feasible water ranges in Wilmington through 1.8m (5.9ft).
In 2018, when Category 1 Hurricane Florence slammed into Wilmington, water tiers did certainly attain a document 1.1m (3.6ft) above excessive tide. That’s why appreciation altering tides is critical to making ready for the future, Talke says. People are going to proceed to dredge channels and fill in wetlands and in any other case alter our coastal surroundings. Bit by using bit, every change shifts the world in which we live.
1 comments:

Next my spirit heated one, for a cheese fondue, because it is a ceramic pot. fondue set
ReplyDelete
Sports View
5/Sports/slider
It was once the muddy water that caught Stefan Talke’s eye. In the mid-2000s Talke used to be a postdoctoral pupil at Utrecht University, analyzing the river Ems that empties into the North Sea between Germany and the Netherlands. Decades earlier, engineers had begun dredging components of the Ems so that newly constructed ships may want to navigate it from a shipyard upriver.
But these modifications additionally modified the rhythm with which tides ebbed and flowed into the river from the sea. Those moving tides stirred up sediment from the river backside and muddied its waters. Over the ultimate one hundred twenty years the tidal vary – the distance between excessive and low tide – has quintupled in the Ems estuary.
“I had usually assumed tides have been constant,” says Talke, now an oceanographer at California Polytechnic State University in San Luis Obispo. “That’s why we have tide tables.” He used to be amazed to discover, he says, that no longer solely should tides endure long-term changes, however that they ought to trade via so much.
Most humans suppose of tides as ordinary and predictable – the upward jab and fall of coastal waters, precipitated by using the gravitational tug of the Moon and the Sun, forecast down to the minute with a mariner’s tide table. But oceanographers have these days commenced to recognise that tides in many locations round the world are present process splendid changes, in approaches that can’t be defined via interactions amongst celestial bodies.
Rather, it is human beings that are altering the tides. Dredging river channels like the Ems or filling in coastal wetlands can set off shifts. The nature of these shifts is complicated. In some areas the tidal vary grows extra dramatic, whereas in others it shrinks. Either way, the transferring tides have large implications for lots of thousands and thousands of coastal residents.
Perhaps the largest project is how altering tides may add to the dangers of sea stage rise.
As human beings burn greater fossil fuels and put extra heat-trapping greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, international warming is melting ice caps and inflicting the extent of the oceans to expand. In many coastal cities, seawater is now lapping greater than it ever has. Changing tides should add to that hassle and go away some coasts at even higher danger of flooding. “What human beings don’t recognise is that if tidal vary is increasing, it will exacerbate that even more,” says Ivan Haigh, an oceanographer at the University of Southampton, UK.
The way the water strikes throughout the basin is changing, which is having pretty a profound impact on the tides – Ivan Haigh
Engineers have acknowledged for at least a century that tides can alternate locally. In 1899, builders estimated that tides would make bigger in the river Ems upstream from a weir they deliberate to construct. (After the weir used to be built, the tides did expand about as lots as they have been expecting.)
But solely lately have scientists accrued modern, specific tide-gauge facts from round the world, displaying simply how enormous tidal modifications have become. “It wasn’t actually till about 10 years in the past that we commenced to admire that it’s taking place on a plenty wider level,” says Haigh.
Tides come in countless flavours, which can all eventually be traced again to interactions between the Moon, the Sun and Earth. Each tidal cycle reasons coastal waters to upward jab and fall in a predictable pattern, dictated by way of the orbits of these bodies.
The gravitational tugs of the Moon and the Sun don’t trade over the brief term. But what does trade is the way the Earth’s waters reply to that tugging. Think of tides as repeating waves that soar off landmasses and slosh upriver – every now and then visiting lots of kilo-metres inland, as they do in South America’s Amazon River, the place surfers journey the tidal waves. If you exchange the geometry of the land they slosh round in, you alternate the tides, says Talke.
“It’s like having a one-of-a-kind dimension or structure of a bathtub or a swimming pool – you’d assume water to drift otherwise in it,” he says.
In that sense, it’s no longer terribly shocking that tides have modified dramatically in locations the place humans have modified the structure of the underwater landscape. Along the Cape Fear river in North Carolina, dredging to deepen a ship channel has brought about the tidal vary in the town of Wilmington to double, to 1.55m (5.1ft), considering that the 1880s. The identical is proper for Jacksonville, Florida, which sits alongside the dredged St Johns River.
In Sacramento, California, tides disappeared in the late 1800s after mining from the Gold Rush despatched silt speeding downstream. Later, dredging of the Sacramento River added the tides back. And in the Thames estuary that runs thru London, engineers have narrowed and deepened the river over centuries – its tidal vary has multiplied from round 2m (6.6ft) in the time of the Romans to round 8m (26.2ft) in the Victorian age.
Adding dikes or piers motives water to drift extra turbulently and dissipate its electricity faster, probable dampening tides
Tidal adjustments additionally take place each time flowing water generates greater or much less turbulent power as it strikes thru the landscape, write Talke and a colleague in the current Annual Review of Marine Science. Stripping away underwater plant life reduces drag and lets waters glide greater freely, doubtlessly permitting tides to increase. Adding dikes or piers reasons water to drift greater turbulently and dissipate its power faster, probably dampening tides.
Water depth is any other necessary issue in tidal changes, says Haigh. Because tides propagate as shallow-water waves, they alternate the most anywhere the water is additionally shallow. That’s why the Bay of Fundy, between New Brunswick and Nova Scotia in Canada, has some of the most dramatic tidal levels in the world, with waters rising and falling greater than 11m (36ft) every day. Shallow spots like this are probably to see giant modifications in tidal vary as sea ranges rise, Haigh says.
“The way the water strikes throughout the basin is changing, which is having pretty a profound impact on the tides,” he says.
Changing tides have an effect on coastal residents in many ways. Someone who wishes to sail a tall ship beneath a brief bridge has to wait for simply the proper tidal stipulations whilst all and sundry who needs to construct a riverfront domestic in an estuary has to understand precisely the place the high-tide mark is. Engineers designing a tidal-energy device want to comprehend how a whole lot power they can extract from the water flows. And that’s the place the find out about of altering tides can assist human beings put together for a altering world.
Perhaps most importantly, engineers can analyse altering tides to higher layout for future sea degree rise. One current find out about regarded at the low-lying Pearl River Delta in southern China, which is domestic to extra than 60 million people. Michela De Dominicis, an oceanographer at the National Oceanography Centre in Liverpool, UK, and her colleagues calculated how plenty tidal stages would shift for a range of future situations of sea stage rise.
If sea degree have been to upward shove between 0.5m and 2.1m (1.6-6.9ft) in the delta, then cities in its upstream reaches would see tidal will increase between 0.1m and 0.5m (0.3ft and 1.6ft), the scientists found. Add these numbers collectively and it appears as if water tiers should go up between 0.6m and 2.6m (2-8.5ft).
Several cities in the delta, which includes Guangzhou and Shenzhen, are amongst the world’s most inclined to rising water levels, says De Dominicis. Knowing how excessive the water tiers should upward push can assist planners construct higher limitations and different coastal defences.
Researchers are additionally the usage of laptop fashions to analyse how altering tides and rising sea stages may have an effect on different kinds of coastal flooding. A hurricane’s storm surge, for instance, frequently responds to the altering panorama a great deal as tides do.
In 2016, Talke and his colleagues analysed how storm surge may trade in the Cape Fear River estuary alongside with the altering tides. They calculated that dredging of the ship channel has correctly worsened the doable harm posed via a Category 5 typhoon and raised the best possible feasible water ranges in Wilmington through 1.8m (5.9ft).
In 2018, when Category 1 Hurricane Florence slammed into Wilmington, water tiers did certainly attain a document 1.1m (3.6ft) above excessive tide. That’s why appreciation altering tides is critical to making ready for the future, Talke says. People are going to proceed to dredge channels and fill in wetlands and in any other case alter our coastal surroundings. Bit by using bit, every change shifts the world in which we live.
1 comments:

Next my spirit heated one, for a cheese fondue, because it is a ceramic pot. fondue set
ReplyDelete
Fashion
It was once the muddy water that caught Stefan Talke’s eye. In the mid-2000s Talke used to be a postdoctoral pupil at Utrecht University, analyzing the river Ems that empties into the North Sea between Germany and the Netherlands. Decades earlier, engineers had begun dredging components of the Ems so that newly constructed ships may want to navigate it from a shipyard upriver.
But these modifications additionally modified the rhythm with which tides ebbed and flowed into the river from the sea. Those moving tides stirred up sediment from the river backside and muddied its waters. Over the ultimate one hundred twenty years the tidal vary – the distance between excessive and low tide – has quintupled in the Ems estuary.
“I had usually assumed tides have been constant,” says Talke, now an oceanographer at California Polytechnic State University in San Luis Obispo. “That’s why we have tide tables.” He used to be amazed to discover, he says, that no longer solely should tides endure long-term changes, however that they ought to trade via so much.
Most humans suppose of tides as ordinary and predictable – the upward jab and fall of coastal waters, precipitated by using the gravitational tug of the Moon and the Sun, forecast down to the minute with a mariner’s tide table. But oceanographers have these days commenced to recognise that tides in many locations round the world are present process splendid changes, in approaches that can’t be defined via interactions amongst celestial bodies.
Rather, it is human beings that are altering the tides. Dredging river channels like the Ems or filling in coastal wetlands can set off shifts. The nature of these shifts is complicated. In some areas the tidal vary grows extra dramatic, whereas in others it shrinks. Either way, the transferring tides have large implications for lots of thousands and thousands of coastal residents.
Perhaps the largest project is how altering tides may add to the dangers of sea stage rise.
As human beings burn greater fossil fuels and put extra heat-trapping greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, international warming is melting ice caps and inflicting the extent of the oceans to expand. In many coastal cities, seawater is now lapping greater than it ever has. Changing tides should add to that hassle and go away some coasts at even higher danger of flooding. “What human beings don’t recognise is that if tidal vary is increasing, it will exacerbate that even more,” says Ivan Haigh, an oceanographer at the University of Southampton, UK.
The way the water strikes throughout the basin is changing, which is having pretty a profound impact on the tides – Ivan Haigh
Engineers have acknowledged for at least a century that tides can alternate locally. In 1899, builders estimated that tides would make bigger in the river Ems upstream from a weir they deliberate to construct. (After the weir used to be built, the tides did expand about as lots as they have been expecting.)
But solely lately have scientists accrued modern, specific tide-gauge facts from round the world, displaying simply how enormous tidal modifications have become. “It wasn’t actually till about 10 years in the past that we commenced to admire that it’s taking place on a plenty wider level,” says Haigh.
Tides come in countless flavours, which can all eventually be traced again to interactions between the Moon, the Sun and Earth. Each tidal cycle reasons coastal waters to upward jab and fall in a predictable pattern, dictated by way of the orbits of these bodies.
The gravitational tugs of the Moon and the Sun don’t trade over the brief term. But what does trade is the way the Earth’s waters reply to that tugging. Think of tides as repeating waves that soar off landmasses and slosh upriver – every now and then visiting lots of kilo-metres inland, as they do in South America’s Amazon River, the place surfers journey the tidal waves. If you exchange the geometry of the land they slosh round in, you alternate the tides, says Talke.
“It’s like having a one-of-a-kind dimension or structure of a bathtub or a swimming pool – you’d assume water to drift otherwise in it,” he says.
In that sense, it’s no longer terribly shocking that tides have modified dramatically in locations the place humans have modified the structure of the underwater landscape. Along the Cape Fear river in North Carolina, dredging to deepen a ship channel has brought about the tidal vary in the town of Wilmington to double, to 1.55m (5.1ft), considering that the 1880s. The identical is proper for Jacksonville, Florida, which sits alongside the dredged St Johns River.
In Sacramento, California, tides disappeared in the late 1800s after mining from the Gold Rush despatched silt speeding downstream. Later, dredging of the Sacramento River added the tides back. And in the Thames estuary that runs thru London, engineers have narrowed and deepened the river over centuries – its tidal vary has multiplied from round 2m (6.6ft) in the time of the Romans to round 8m (26.2ft) in the Victorian age.
Adding dikes or piers motives water to drift extra turbulently and dissipate its electricity faster, probable dampening tides
Tidal adjustments additionally take place each time flowing water generates greater or much less turbulent power as it strikes thru the landscape, write Talke and a colleague in the current Annual Review of Marine Science. Stripping away underwater plant life reduces drag and lets waters glide greater freely, doubtlessly permitting tides to increase. Adding dikes or piers reasons water to drift greater turbulently and dissipate its power faster, probably dampening tides.
Water depth is any other necessary issue in tidal changes, says Haigh. Because tides propagate as shallow-water waves, they alternate the most anywhere the water is additionally shallow. That’s why the Bay of Fundy, between New Brunswick and Nova Scotia in Canada, has some of the most dramatic tidal levels in the world, with waters rising and falling greater than 11m (36ft) every day. Shallow spots like this are probably to see giant modifications in tidal vary as sea ranges rise, Haigh says.
“The way the water strikes throughout the basin is changing, which is having pretty a profound impact on the tides,” he says.
Changing tides have an effect on coastal residents in many ways. Someone who wishes to sail a tall ship beneath a brief bridge has to wait for simply the proper tidal stipulations whilst all and sundry who needs to construct a riverfront domestic in an estuary has to understand precisely the place the high-tide mark is. Engineers designing a tidal-energy device want to comprehend how a whole lot power they can extract from the water flows. And that’s the place the find out about of altering tides can assist human beings put together for a altering world.
Perhaps most importantly, engineers can analyse altering tides to higher layout for future sea degree rise. One current find out about regarded at the low-lying Pearl River Delta in southern China, which is domestic to extra than 60 million people. Michela De Dominicis, an oceanographer at the National Oceanography Centre in Liverpool, UK, and her colleagues calculated how plenty tidal stages would shift for a range of future situations of sea stage rise.
If sea degree have been to upward shove between 0.5m and 2.1m (1.6-6.9ft) in the delta, then cities in its upstream reaches would see tidal will increase between 0.1m and 0.5m (0.3ft and 1.6ft), the scientists found. Add these numbers collectively and it appears as if water tiers should go up between 0.6m and 2.6m (2-8.5ft).
Several cities in the delta, which includes Guangzhou and Shenzhen, are amongst the world’s most inclined to rising water levels, says De Dominicis. Knowing how excessive the water tiers should upward push can assist planners construct higher limitations and different coastal defences.
Researchers are additionally the usage of laptop fashions to analyse how altering tides and rising sea stages may have an effect on different kinds of coastal flooding. A hurricane’s storm surge, for instance, frequently responds to the altering panorama a great deal as tides do.
In 2016, Talke and his colleagues analysed how storm surge may trade in the Cape Fear River estuary alongside with the altering tides. They calculated that dredging of the ship channel has correctly worsened the doable harm posed via a Category 5 typhoon and raised the best possible feasible water ranges in Wilmington through 1.8m (5.9ft).
In 2018, when Category 1 Hurricane Florence slammed into Wilmington, water tiers did certainly attain a document 1.1m (3.6ft) above excessive tide. That’s why appreciation altering tides is critical to making ready for the future, Talke says. People are going to proceed to dredge channels and fill in wetlands and in any other case alter our coastal surroundings. Bit by using bit, every change shifts the world in which we live.
1 comments:

Next my spirit heated one, for a cheese fondue, because it is a ceramic pot. fondue set
ReplyDelete
Business
Categories
Ad Code
World Fresh Updates
4/sgrid/recent
Most Viewed
4/sgrid/recent
Trending
12/recent/slide-posts
Carousel
Column Left
Post Top Ad
Responsive Ads Here
Search This Blog
Social Sharing
Post Top Ad
Responsive Ads Here
Fitness
8/Health/grid-big
Business
6/lgrid/recent
Gadgets News
4/footer/recent
Copyright @ 2020 by TTIN
Ad Space
Post Top Ad
Responsive Ads Here
Cities & Locals
5/col-left/recent
Sports & Games
5/col-right/recent
Editor Updates
megagrid/recent
category1
Followers
Author Social Links
Categories
Tags Clouds
Footer Copyright
Design by - Blogger Templates | Distributed by BloggerTemplate.org
Translate
Top Post Ad
The Relaxation Time
Post Top Ad


Popular Posts
Below Post Ad
Featured Grid Widget
Author Details
Hey there, We are Blossom Themes! We are trying to provide you the new way to look and use the blogger templates. Our designers are working hard and pushing the boundaries of possibilities to widen the horizon of the regular templates and provide high quality blogger templates to all hardworking bloggers!
Tech Life
Typhoon Haishen drew nearer to Japan's southern mainland on Sunday, prompting authorities to suggest evacuation and warn of probably record rainfall, extraordinary wind, excessive tides and massive ocean swells. According to the Fire and Disaster Management Agency (FDMA), authorities have advised more than 100,000 families in the southern areas of Okinawa, Kagoshima, Kumamoto and Nagasaki to evacuate soon. The storm has reduce electricity to greater than 3,000 residences in Okinawa, the southernmost island prefecture, and extra than 8,000 houses in Amamioshima, in accordance to country wide broadcaster NHK. Two accidents have been reported, in accordance to the FDMA, however authorities had been advising the easiest stages of warning for a typhoon. "Areas the place the storm passes are anticipated to see file excessive winds and waves," a meteorological reputable advised a nationally televised information convention on Sunday. " You wouldn't be able to go to a ...
A Black Hole Collided With Something That Shouldn't Exist
Astronomers are difficult over observations that exhibit a black gap smashing into a thriller object of uncommon size. New lookup posted in The Astrophysical Journal Letters describes a collision between a black gap and a yet-to-be recognized object. At the time of this celestial tryst, the black gap was once 23 instances greater huge than our Sun, however the unknown object used to be simply 2.6 instances the Sun’s mass, which is incredibly weird. The scientists at the back of the new paper, co-authored through astrophysicist Vicky Kalogera from Northwestern University, say the smaller object should be a black gap or a neutron star, the latter of which is the super-dense remnant of an exploded star. A black gap of 2.6 photo voltaic hundreds would be the smallest on file (the lightest acknowledged black gap is 5 photo voltaic masses), whilst a neutron megastar of the identical mass would be the largest on file (the heaviest neutron stars are between 2.3 and 2.4 photo voltaic masses). S...
Lionel Messi announced to stay at Barcelona
Lionel Messi has confirmed he will remain at Barcelona due to the fact the economic outlay required to make his preferred exit a fact used to be "impossible". The Argentina celebrity despatched shockwaves thru Camp Nou final week when he introduced he desired to depart Barca in the wake of the humiliating 8-2 loss to Bayern Munich in the Champions League quarter-finals. Messi was once of the faith he may want to depart on a free switch after activating a clause permitting him to terminate his contract at the give up of the season, with Manchester City shortly rising as favourites for his signature. La Liga has rejected the claim, insisting that any potential sweater would have to negotiate with Barca or pay a 700 700 million launch clause in Messi's contract, choosing June 10. Will choose to go for something without ending. Messi's father and agent Jorge met Barca president Josep Maria Bartomeu to talk about the six-time Ballon d'Or winner's future on Wednesda...
Featured Section
Post Top Ad
























1 Comments
Next my spirit heated one, for a cheese fondue, because it is a ceramic pot. fondue set
ReplyDeletePlease do not enter any spam links in the comment box.